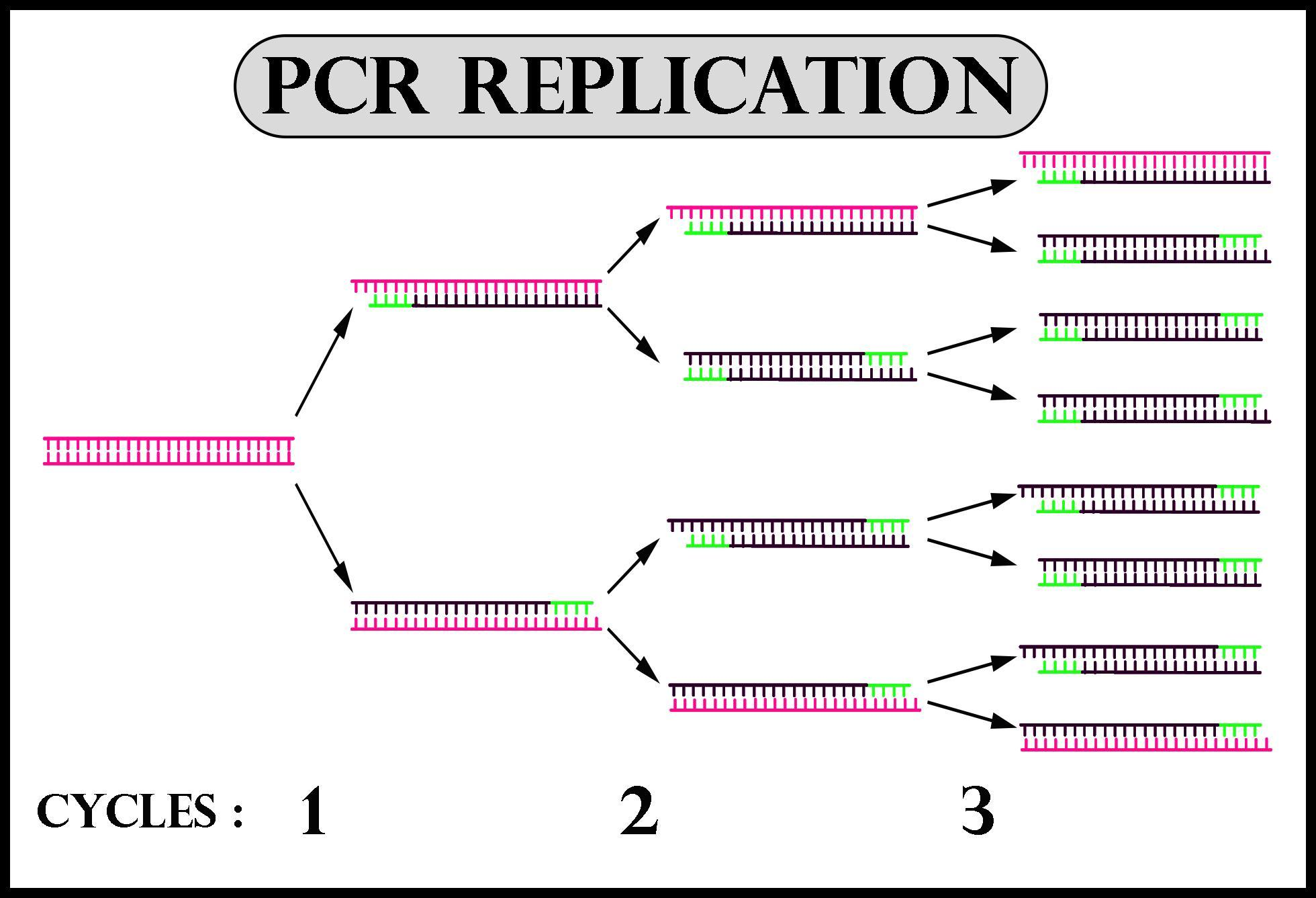
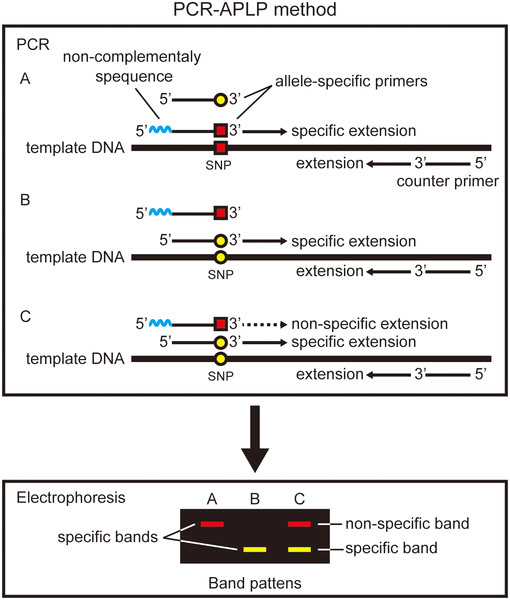
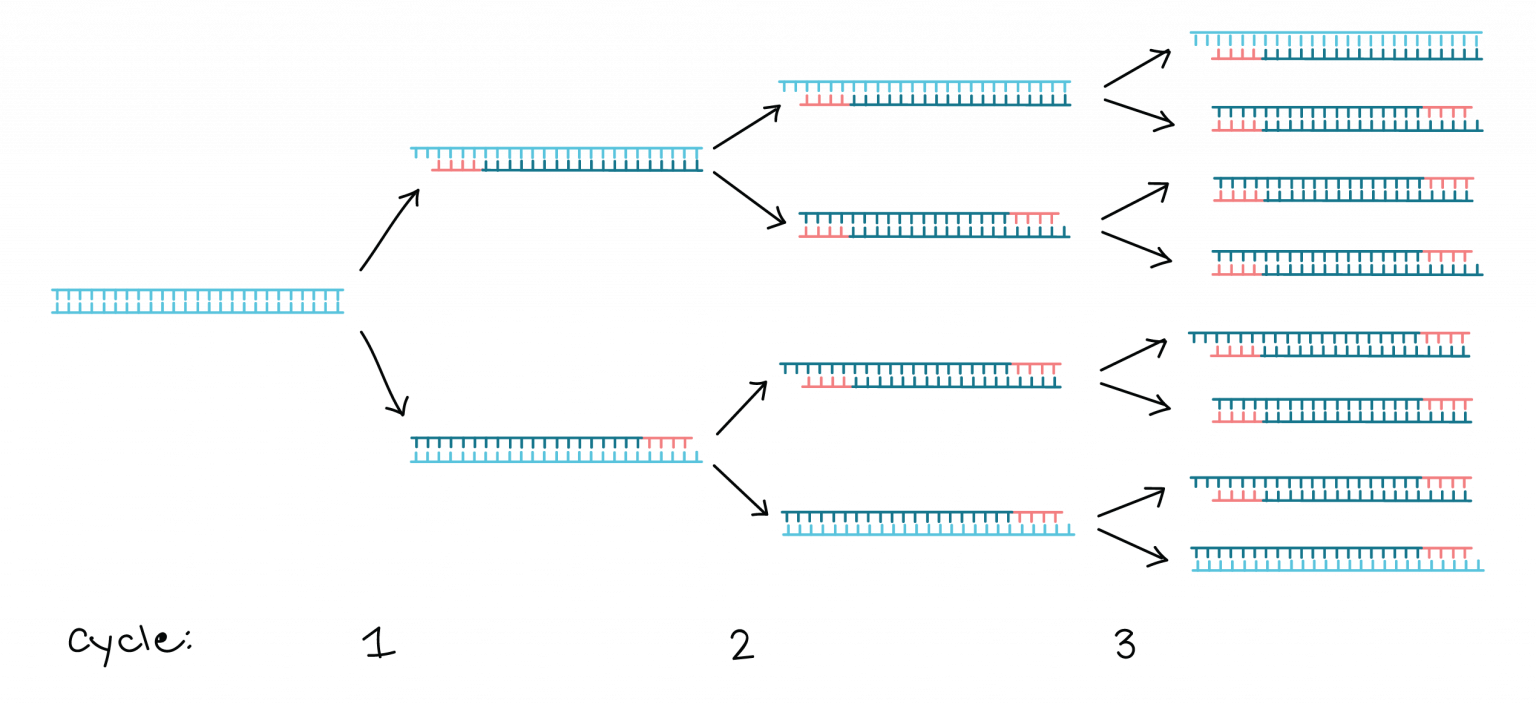
How Much Dna Template For Pcr
How Much Dna Template For Pcr - 50 ng ÷ 6 = 8.3ul of. 0.5 μl phage or 1 μl yeast: 250 bp ÷ 5 = 50ng of dna. Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually a normal pcr reaction can easily. Web 1) generally 50 to 200 ng of dna i have worked with depending upon the gene of interest, for normal pcr of 16s rdna gene amplification i have used as little as 50 ng of dna but. Template total mass (recommended) template volume per reaction: During a typical pcr, template dna (containing the region of interest) is mixed with. For plasmid dna the size is the entire plasmid, vector. Dna length (include vector) template concentration in 10 µl: As an initial guide, spectrophotometric and molar conversion values for different nucleic acid. Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually a normal pcr reaction can easily. Web in pcr, the length of the target dna sequence is usually between 100bp to 5,000bp. Web 1) generally 50 to 200 ng of dna i have worked with depending upon. Web the appropriate amount of master mix can be pipetted into tubes or plate wells and combined with any components that vary among the reactions, such as dna or rna. Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually a normal pcr reaction can easily. Web. Web the most commonly used dna polymerases for pcr have no reverse transcriptase activity under standard reaction conditions, and thus, amplification products will be generated. 0.5 μl phage or 1 μl yeast: Web you want to sequence a 250 bp pcr product. 250 bp ÷ 5 = 50ng of dna. Web generally, no more than 1 ug of template dna. Web the following table lists the recommended amount of dna template and primer for optimal sanger sequencing results. As an initial guide, spectrophotometric and molar conversion values for different nucleic acid. Web the most commonly used dna polymerases for pcr have no reverse transcriptase activity under standard reaction conditions, and thus, amplification products will be generated. Web generally, no more. Design your primer per the pcr primer design general. Template total mass (recommended) template volume per reaction: For plasmid dna the size is the entire plasmid, vector. Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually a normal pcr reaction can easily. You need 50ng of. Web the appropriate amount of master mix can be pipetted into tubes or plate wells and combined with any components that vary among the reactions, such as dna or rna. 250 bp ÷ 5 = 50ng of dna. You need 50ng of dna. 13 μl ~10 7 molecules phage or ~10 5 molecules yeast: Web we generally recommend using phusion. When the dna is in the log linear phase of amplification, the amount of fluorescence increases above the. 0.5 μl phage or 1 μl yeast: Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually a normal pcr reaction can easily. Web we generally recommend using phusion. Dna length (include vector) template concentration in 10 µl: Web you want to sequence a 250 bp pcr product. Web we generally recommend using phusion dna polymerase at a concentration of 20 units/ml (1.0 units/50 μl reaction). Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually. Design your primer per the pcr primer design general. 2 ng/μl phage or 10 ng/μl yeast: As an initial guide, spectrophotometric and molar conversion values for different nucleic acid. Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually a normal pcr reaction can easily. Web the. Web during dna replication, the template is generated by enzymes known as helicases. Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually a normal pcr reaction can easily. Web 1) generally 50 to 200 ng of dna i have worked with depending upon the gene of. As an initial guide, spectrophotometric and molar conversion values for different nucleic acid. 50 ng ÷ 6 = 8.3ul of. 250 bp ÷ 5 = 50ng of dna. For plasmid dna the size is the entire plasmid, vector. During a typical pcr, template dna (containing the region of interest) is mixed with. You need 50ng of dna. 0.5 μl phage or 1 μl yeast: Design your primer per the pcr primer design general. Web the amount of template to be used depends on the molecular weight (and hence the number of copies) of your construct, usually a normal pcr reaction can easily. Web the following table lists the recommended amount of dna template and primer for optimal sanger sequencing results. When the dna is in the log linear phase of amplification, the amount of fluorescence increases above the. Template total mass (recommended) template volume per reaction: Web we generally recommend using phusion dna polymerase at a concentration of 20 units/ml (1.0 units/50 μl reaction). Web you want to sequence a 250 bp pcr product. If your 250 bp pcr product has a concentration of 6ng/ul. Web the most commonly used dna polymerases for pcr have no reverse transcriptase activity under standard reaction conditions, and thus, amplification products will be generated. 2 ng/μl phage or 10 ng/μl yeast: Web in pcr, the length of the target dna sequence is usually between 100bp to 5,000bp. This technique involves 0.1 m potassium hydroxide. Web the appropriate amount of master mix can be pipetted into tubes or plate wells and combined with any components that vary among the reactions, such as dna or rna. This technique involves 0.1 m potassium hydroxide. If your 250 bp pcr product has a concentration of 6ng/ul. Web in pcr, the length of the target dna sequence is usually between 100bp to 5,000bp. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a method to rapidly amplify sequences of dna. Web generally, no more than 1 ug of template dna should be used per pcr reaction. Web the most commonly used dna polymerases for pcr have no reverse transcriptase activity under standard reaction conditions, and thus, amplification products will be generated. However, the optimal concentration of phusion dna. You need 50ng of dna. For plasmid dna the size is the entire plasmid, vector. Web in quantitative pcr, dna amplification is monitored at each cycle of pcr. 13 μl ~10 7 molecules phage or ~10 5 molecules yeast: Dna length (include vector) template concentration in 10 µl: Template total mass (recommended) template volume per reaction: Web 1) generally 50 to 200 ng of dna i have worked with depending upon the gene of interest, for normal pcr of 16s rdna gene amplification i have used as little as 50 ng of dna but. Web the appropriate amount of master mix can be pipetted into tubes or plate wells and combined with any components that vary among the reactions, such as dna or rna. 250 bp ÷ 5 = 50ng of dna.PCR process Dna, Dna drawing, Biology notes
What are the properties of PCR (template) DNA? Education
How many copies of DNA samples are produced in the class 12 biology CBSE
Schematic diagram of PCR showing that each cycle contains three steps
Fun with Biotechnology PCR
How Much Template Dna for Pcr williamsonga.us
How Much Template Dna for Pcr williamsonga.us
How To Design Primers For Pcr Amplification
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Definition, Steps, Principle, Application
Overview of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Template DNA strands
Web You Want To Sequence A 250 Bp Pcr Product.
Web The Amount Of Template To Be Used Depends On The Molecular Weight (And Hence The Number Of Copies) Of Your Construct, Usually A Normal Pcr Reaction Can Easily.
Web We Generally Recommend Using Phusion Dna Polymerase At A Concentration Of 20 Units/Ml (1.0 Units/50 Μl Reaction).
2 Ng/Μl Phage Or 10 Ng/Μl Yeast:
Related Post: